Gaining Visibility into Your Network Topology
When you build your Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Network by launching Aviatrix Gateways and other constructs, Aviatrix CoPilot automatically draws a topology map that shows your current network environment. In Topology, you can search for any objects that are plotted. This allows you to quickly isolate and identify resources that you are looking for in your entire environment and across clouds.
You can run diagnostics from any Aviatrix gateway running in your multicloud network directly from Topology. Performing diagnostics from Topology can dramatically reduce the time spent troubleshooting issues.
You can use filters to show only the parts of your network environment you want to see. You can use many different properties of your managed resources to filter them.
Working with Topology
This section describes the Topology feature of Aviatrix CoPilot.
Topology provides a visual representation of deployed networks, gateways, instances, and gateway connections.
The Topology feature gives you visibility into your network as follows:
-
Network Graph - Network View
In Network Graph, in Network view, CoPilot displays a network topology map that shows the logical and physical layout of how managed network resources are connected across multiple clouds. Topology provides a visual representation of deployed networks (VPCs/VNets/VCNs), gateways, instances, and gateway connections. CoPilot automatically draws the map when it connects to Aviatrix Controller.
The Aviatrix Gateways running in your multicloud network enable you to run diagnostics from them directly from Topology. When highlighting a gateway, click on the DIAG button to see options available for performing diagnostics from the gateway that is in focus.
-
Network Graph - Transit View
In Network Graph, in Transit view, CoPilot shows the topology of your Aviatrix transit network in relation to your deployed Aviatrix transit gateways. By clicking on the Aviatrix transit icon, you can see all of the transit VPCs/VNets that are managed by Aviatrix Controller. By clicking on a region icon, you can see the spoke VPC/VNets that the controller currently manages. By clicking on a spoke VPC/VNet, you can see all network constructs inside of that spoke. You can use the search field to find specific resources.
-
Topology Replay
In Topology Replay, CoPilot shows what changed in your environment and when it changed. CoPilot shows when route, credential, and other metrics in your cloud network constructs have changed over time. A timeline panel shows you all of the changes (as change sets) that were recorded over the last month. You can analyze the additions, modifications, and deletions recorded in each change set. You can delete change sets when you no longer need them.
You can click the New Topology Experience toggle to see a version of the map introduced in CoPilot release 3.0.2 (Topology New Experience). See New Topology Experience.
Show Managed Resources by Using Filters
You can filter your network managed resources in the topology map to show only the resources you want by using filters.
To create a topology filter, see:
Topology Resource Field Reference
In Topology, the topology map’s supported filter fields include identifiers and tags for constructs, health and status metrics, and associative properties like CSP Vendor and Region. This section describes the properties of managed resources you can filter on in the map for Transit VPC/VNets, Spoke VPCs, Aviatrix transit gateways, Aviatrix spoke gateways, AWS TGWs, and user instances (virtual machines).
The technical descriptions are for Topology New Experience.
Transit VPC/VNet Field Reference
You can filter your Transit VPC/VNet topology in the topology map using the following fields for Transit VPCs.
| Transit VPC/VNet Property | Description |
|---|---|
Account Name |
The CSP Account associated with this VPC. |
Cloud |
The CSP that this VPC/VNet belongs to (AWS, Azure, etc.). |
Managed |
Whether or not this VPC is managed by an Aviatrix Gateway. |
Name |
The VPC’s name tag. |
NAT Gateways |
List of the VPC’s NAT Gateways. |
Peer Connections |
List of the VPC’s peer connections. |
Region |
The CSP region where the VPC is located. |
Site2Cloud Connections |
List of the VPC’s Site2Cloud tunnels. |
Type |
The type of Topology construct this is (VPC, in this case). |
Virtual Machines |
Number of VM’s (instances) the VPC contains. |
VPC CIDR |
List of the VPC’s CIDRs. |
VPC ID |
The VPC’s unique identifier. |
Spoke VPC/VNet Field Reference
You can filter your Spoke VPC topology in the topology map using the following fields for Spoke VPC/VNets.
| Spoke VPC/VNet Property | Description |
|---|---|
Account Name |
The CSP Account associated with this VPC. |
Cloud |
The CSP that this VPC/VNet belongs to (AWS, Azure, etc.). |
Managed |
Whether or not this VPC is managed by an Aviatrix Gateway. |
Name |
The VPC’s name tag. |
NAT Gateways |
List of the VPC’s NAT Gateways. |
Peer Connections |
List of the VPC’s peer connections. |
Region |
The CSP region where the VPC is located. |
Site2Cloud Connections |
List of the VPC’s Site2Cloud tunnels. |
Type |
The type of Topology construct this is (VPC, in this case). |
Virtual Machines |
Number of VM’s (instances) the VPC contains. |
VPC CIDR |
List of the VPC’s CIDRs. |
VPC ID |
The VPC’s unique identifier. |
Transit Gateway Field Reference
You can filter your Transit Gateway topology in the topology map using the following fields for Transit Gateways virtual machines.
| Transit Gateway VM Field | Description |
|---|---|
Account Name |
The CSP Account associated with this VPC. |
Associated Gateway |
The Aviatrix Gateway with which this VM is associated. |
Cloud |
The CSP that this VPC belongs to (AWS, Azure, etc.). |
Hypervisor |
The instance’s hypervisor. |
Image ID |
ID of the image from which the instance was built. |
Insane Mode (High Performance Encryption Mode) |
Whether the gateway has high performance encryption active. |
Instance ID |
ID of the image from which the instance was built. |
Instance Size |
The size of the instance (e.g. “t2.micro,"). |
Kernel |
The Linux kernel version of the Gateway instance. |
Launch Time |
The timestamp when the VM (Gateway in this case) was launched. |
License Expiry |
The timestamp when the gateway’s license expires. |
License ID |
The unique identifier of the instance’s license. |
Name |
The name of the instance. |
Private IP |
The private IP of the instance. |
Private DNS Name |
The Private DNS name of the instance. |
Public DNS Name |
The Public DNS name of the instance. |
Public IP |
The Public IP of the instance. |
Region |
The CSP region in which the instance is located. |
Source NAT |
Denotes whether Source NAT is active on this gateway. |
Stateful Firewall |
Denotes whether stateful firewall rules are enabled or disabled on the gateway. |
Status |
Denotes whether the instance is running. |
Subnet ID |
The ID of the instance’s subnet. |
Type |
The type of Topology construct this is (VPC, in this case). |
VPC ID |
The ID of the instance’s VPC. |
VPC Name |
The name of the instance’s VPC. |
Spoke Gateway Field Reference
You can filter your Spoke Gateway topology in the topology map using the following fields for Spoke Gateways virtual machines.
| Spoke Gateway VM Field | Description |
|---|---|
Account Name |
The CSP Account associated with this VPC. |
Associated Gateway |
The Aviatrix Gateway with which this VM is associated. |
Cloud |
The CSP that this VPC belongs to (AWS, Azure, etc.). |
Hypervisor |
The instance’s hypervisor. |
Image ID |
ID of the image from which the instance was built. |
Insane Mode (High Performance Encryption Mode) |
Whether the gateway has high performance encryption active. |
Instance ID |
ID of the image from which the instance was built. |
Instance Size |
The size of the instance (e.g. “t2.micro,"). |
Kernel |
The Linux kernel version of the Gateway instance. |
Launch Time |
The timestamp when the VM (Gateway in this case) was launched. |
License Expiry |
The timestamp when the gateway’s license expires. |
License ID |
The unique identifier of the instance’s license. |
Name |
The name of the instance. |
Private IP |
The private IP of the instance. |
Private DNS Name |
The Private DNS name of the instance. |
Public DNS Name |
The Public DNS name of the instance. |
Public IP |
The Public IP of the instance. |
Region |
The CSP region in which the instance is located. |
Source NAT |
Denotes whether Source NAT is active on this gateway. |
Stateful Firewall |
Denotes whether stateful firewall rules are enabled or disabled on the gateway. |
Status |
Denotes whether the instance is running. |
Subnet ID |
The ID of the instance’s subnet. |
Type |
The type of Topology construct this is (Virtual Machine, in this case). |
VPC ID |
The ID of the instance’s VPC. |
VPC Name |
The name of the instance’s VPC. |
AWS TGW Field Reference
You can filter your AWS TGW topology in the topology map using the following fields for AWS TGWs.
| AWS TGW Property | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
The name of the AWS Transit Gateway. |
Account Name |
The Aviatrix account that corresponds to an IAM role or account in AWS. |
Region |
One of the AWS regions. |
AWS TGW ASN |
TGW ASN number. The default AS number is 64512. |
AWS TGW CIDR |
The TGW CIDR ranges. |
Instance ID |
ID of the image from which the AWS TGW was built. |
User Virtual Machine Field Reference
You can filter your Virtual Machine topology in the topology map using the following fields for user virtual machines that are in Aviatrix-managed VPCs/VNets.
| User Virtual Machine Field | Description |
|---|---|
Account Name |
The CSP Account associated with this VPC. |
Associated Gateway |
The Aviatrix Gateway with which this VM is associated. |
Cloud |
The CSP that this VPC belongs to (AWS, Azure, etc.). |
Hypervisor |
The instance’s hypervisor. |
Image ID |
ID of the image from which the instance was built. |
Instance ID |
ID of the image from which the instance was built. |
Instance Size |
The size of the instance (e.g. “t2.micro,"). |
Kernel |
The Linux kernel version of the Gateway instance. |
Launch Time |
The timestamp when the VM (Gateway in this case) was launched. |
Name |
The name of the instance. |
Private IP |
The private IP of the instance. |
Private DNS Name |
The Private DNS name of the instance. |
Public DNS Name |
The Public DNS name of the instance. |
Public IP |
The Public IP of the instance. |
Region |
The CSP region in which the instance is located. |
Status |
Denotes whether the instance is running. |
Subnet ID |
The ID of the instance’s subnet. |
Type |
The type of Topology construct this is (Virtual Machine, in this case). |
VPC ID |
The ID of the instance’s VPC. |
VPC Name |
The name of the instance’s VPC. |
Subnets Field Reference
You can filter your Subnet topology in the topology map using the following fields for subnets that are Aviatrix-managed.
| Subnet Field | Description |
|---|---|
Account Name |
The CSP Account associated with this VPC. |
Cloud |
The CSP that this VPC belongs to (AWS, Azure, etc.). |
Interface ID |
The ID of the gateway interface the subnet is on. |
Name |
The name of the subnet. |
Region |
The CSP region in which the instance is located. |
Subnet CIDR |
The CIDR of the subnet. |
Subnet ID |
The ID of the instance’s subnet |
Type |
The type of Topology construct this is (Subnet, in this case). |
VPC ID |
The ID of the instance’s VPC. |
VPC Name |
The name of the instance’s VPC. |
Latencies for Links in Your Network Topology
In CoPilot > Topology map (New Topology Experience), you can see link status for links between gateways located in different VPC/VNets.
A green line indicates less than 50 milliseconds of latency for the link.
A brown line indicates between 50 and 100 milliseconds of latency for the link.
A red line indicates more than 50 milliseconds of latency for the link.
Viewing a Map of your Network Topology
When you build your Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Network by launching Aviatrix Gateways and other constructs, Aviatrix CoPilot automatically draws a map to show your current network topology.
To view the topology map, go to Networking > Topology or type Topology in the navigation search.
You can filter the topology map on multiple fields to show only the gateways and constructs you want to see in your network. You can save the conditions to create a topology filter.
Working with Topology
This section describes the Topology feature of Aviatrix CoPilot.
Topology provides a visual representation of deployed networks, gateways, instances, and gateway connections.
The Topology feature gives you visibility into your network as follows:
-
Network Graph - Network View
In Network Graph, in Network view, CoPilot displays a network topology map that shows the logical and physical layout of how managed network resources are connected across multiple clouds. Topology provides a visual representation of deployed networks (VPCs/VNets/VCNs), gateways, instances, and gateway connections. CoPilot automatically draws the map when it connects to Aviatrix Controller.
The Aviatrix Gateways running in your multicloud network enable you to run diagnostics from them directly from Topology. When highlighting a gateway, click on the DIAG button to see options available for performing diagnostics from the gateway that is in focus.
-
Network Graph - Transit View
In Network Graph, in Transit view, CoPilot shows the topology of your Aviatrix transit network in relation to your deployed Aviatrix transit gateways. By clicking on the Aviatrix transit icon, you can see all of the transit VPCs/VNets that are managed by Aviatrix Controller. By clicking on a region icon, you can see the spoke VPC/VNets that the controller currently manages. By clicking on a spoke VPC/VNet, you can see all network constructs inside of that spoke. You can use the search field to find specific resources.
-
Topology Replay
In Topology Replay, CoPilot shows what changed in your environment and when it changed. CoPilot shows when route, credential, and other metrics in your cloud network constructs have changed over time. A timeline panel shows you all of the changes (as change sets) that were recorded over the last month. You can analyze the additions, modifications, and deletions recorded in each change set. You can delete change sets when you no longer need them.
You can click the New Topology Experience toggle to see a new version of the map introduced in CoPilot release 3.0.2 (Topology New Experience). See Topology Map (Topology New Experience) for information about tne new topology map.
Topology Map (New Topology Experience)
In CoPilot release 3.0.1, a new topology map was introduced (Topology New Experience). Use the New Topology Experience toggle to switch to the new map. The new map can display large network topologies.
The illustration below shows the network constructs that get laid out in the 5 circles of the map.
The following constructs are placed on the circle working from the most outer circle to the most inner circle:
1) External Connections (S2C) (outermost circle)
2) Instances
3) Subnets
4) Spoke Gateway VPC/VNets
5) Transit Gateway VPC/VNets (innermost circle)
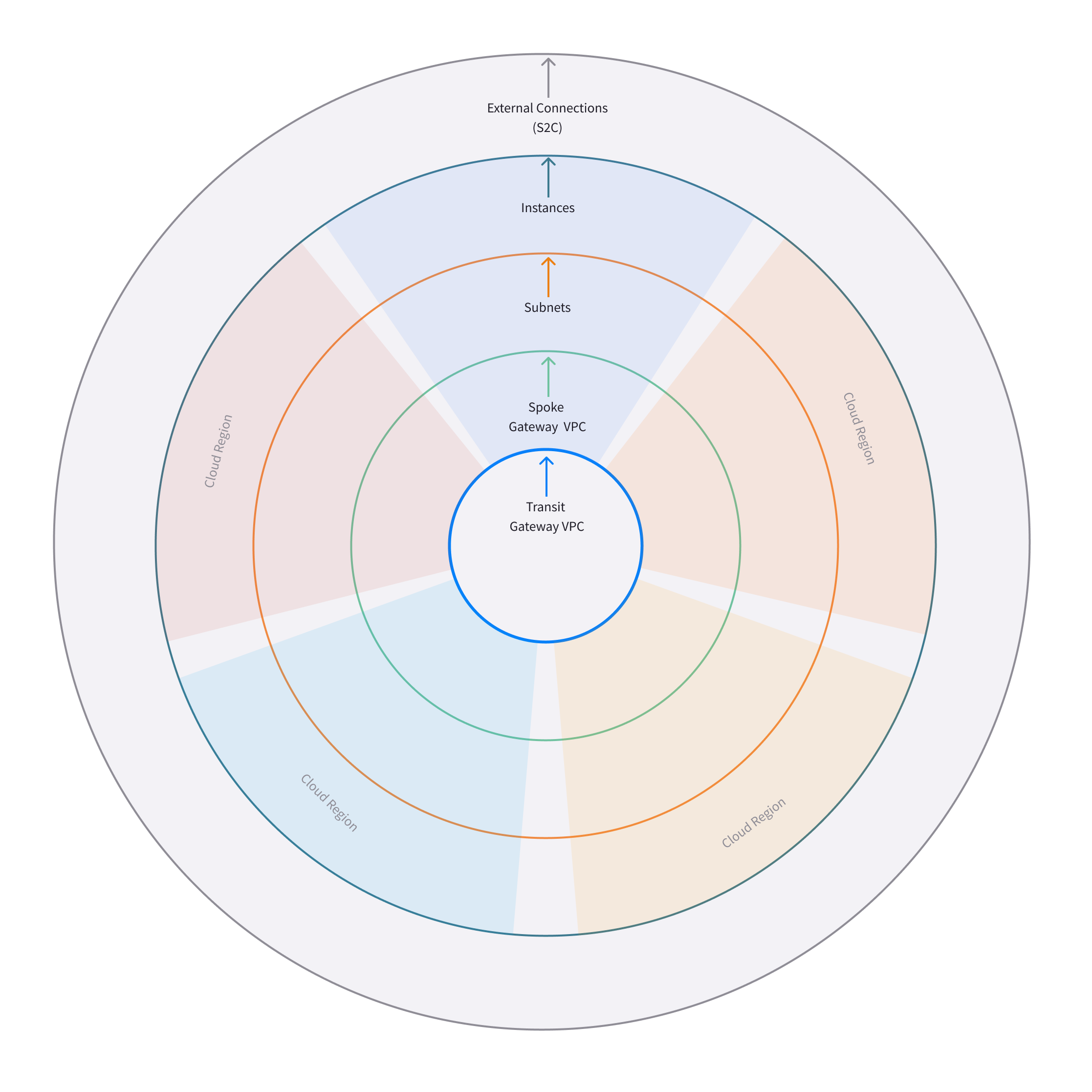
The following illustration shows a topology map populated with nodes that represent the constructs in the network architecture:
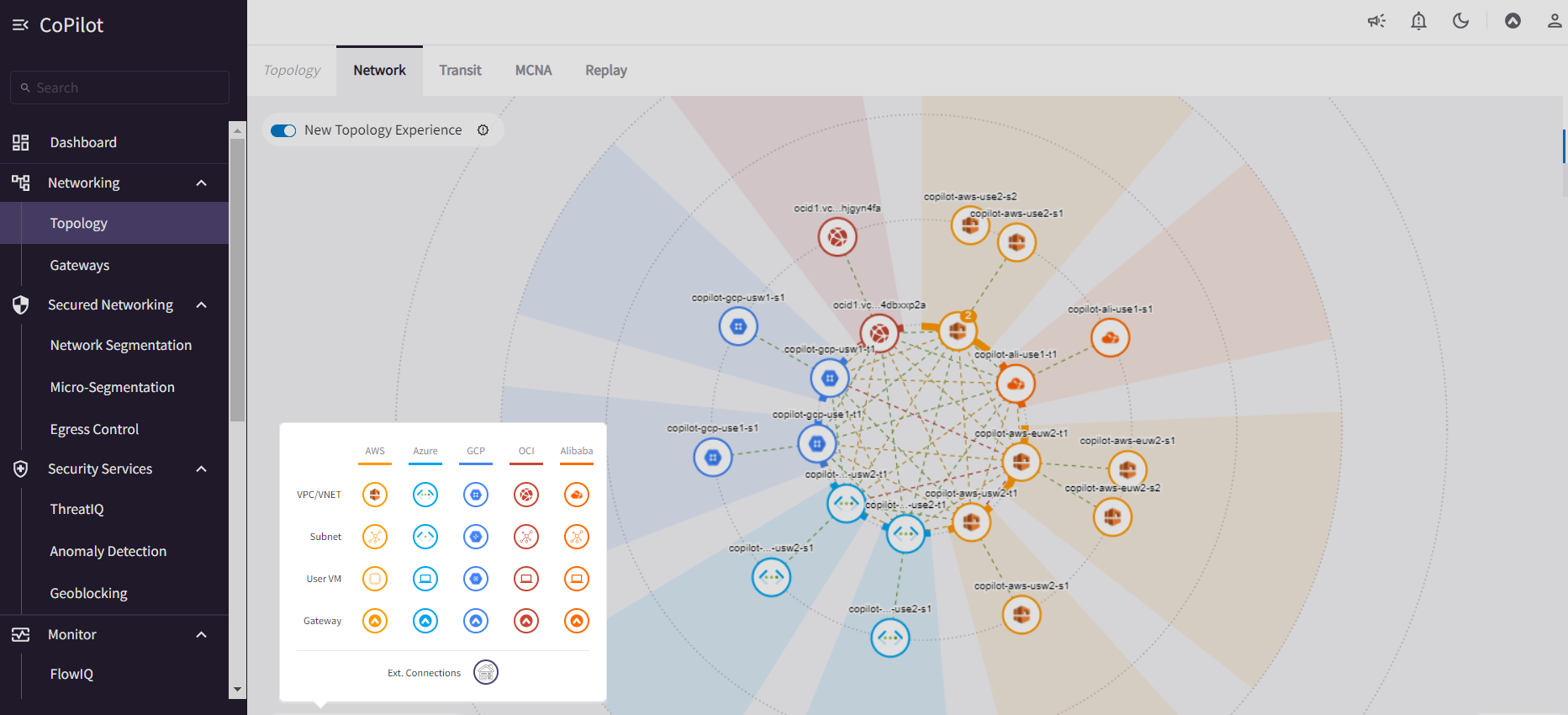
You can apply any number of filters to search for resources in the map.
Topology Map Controls
The following shows the zoom-in, zoom-out, node-expand, and node-collapse topology controls.

For large topologies that have many constructs, you can zoom in to the map for selection of granular nodes to display their properties.
For smaller monitors, you can zoom out of the map to better see the external connections in the outermost circle.
By default, all nodes for your constructs are plotted on the map when you open the Topology page. You can show or hide all subnets and instances under VPC/VNets in your map by using the expand-node and collapse-node controls.
Diagnostics Tools from Topology Map
You can select gateway instances in your Topology map and then click the Tools button below the Properties table, to run relevant diagnostics on those instances.
Creating and saving topology filters (Classic Topology)
Create filters to narrow down the network constructs to include in your topology maps and save the filters to your local system.
To create and save filters for topology, use the following steps:
-
In CoPilot, go to CoPilot > Cloud Fabric > Topology.
-
In Network view, click the Toggle Filter slider to enable the topology filter editor page.
-
In Select a Key to Filter on, select a key and value to filter on. You can apply any number of filters to a given filter group.
-
In Filter Group Name, assign a name to your filter/filter group.
-
Click Save.
The filter is saved to your local system.
When you want to view the topology layout for this filter, click Load Filters and select it from the list. If you load more than one filter, the layout of all of them is displayed in the map.
After a filter/filter group is loaded, you can edit or delete it.
Searching and filtering for cloud native custom tags
Search and filter for custom tags you created in your cloud provider environment for your VPC/VNets and instances.
This feature is available starting from Controller release 6.6.
To filter for cloud native VPC/VNet tags and instance tags, use the following steps:
-
In CoPilot, go to CoPilot > Cloud Fabric > Topology.
-
In Network view, click the Toggle Filter slider to enable the topology filter editor page.
-
From the Select a Key to Filter on list, under the CSP Tags category, select the cloud native tag to filter on.
Topology Map (Classic Topology Experience)
This section describes physics options for the classic view of topology map.
Topology Physics Options (Classic Topology Experience)
This section describes the physics options that control how objects move in the network topology map.
| Topology Physics Option | Description |
|---|---|
Physics Enabled |
|
Smooth Edges |
|
Node Repulsion |
|
Central Gravity |
|
Spring Length |
|
Spring Constant |
|
Dampening |
|
Max Velocity |
|
Min Velocity |
|
Interacting with Topology (Classic Topology Experience)
Objects on the topology maps support drag and drop. You can click, drag and drop resources to reorganize the objects.
|
You can multi-select objects for drag and drop by holding control/command key and selecting. |
-
Toggle filter
Enable the filter editor page where you can create and save your own topology filters and filter groups, load them in the map, and edit or delete them.
-
Search
The search box allows you to filter the objects that are plotted on the topology.
-
Filter
Filter menu offers the option to hide/show different categories of the objects to ensure the topology shows only what you care about.
-
Layout
You can save and reload layouts in the topology using the layout menu. If you prefer the topology to load a default layout, you can select one as the default.
-
Physics options
By default topology objects are organized using physics engines. This menu allows you to configure physical gravity settings that manage the placement of objects. You can adjust different parameters, or turn the physics off completely for complete control over placement of the objects.
Stateful representations in Topology (Classic Topology Experience)
Connectivity elements in Topology reflect the state of the object:
-
Connections between Aviatrix gateways are drawn with color codes representing the status of their connections.
-
Aviatrix gateway icons represent the state of the gateway. A gateway that is down is shown as a black line.
-
Tunnels statuses are shown with green or red lines, representing the status of the link.