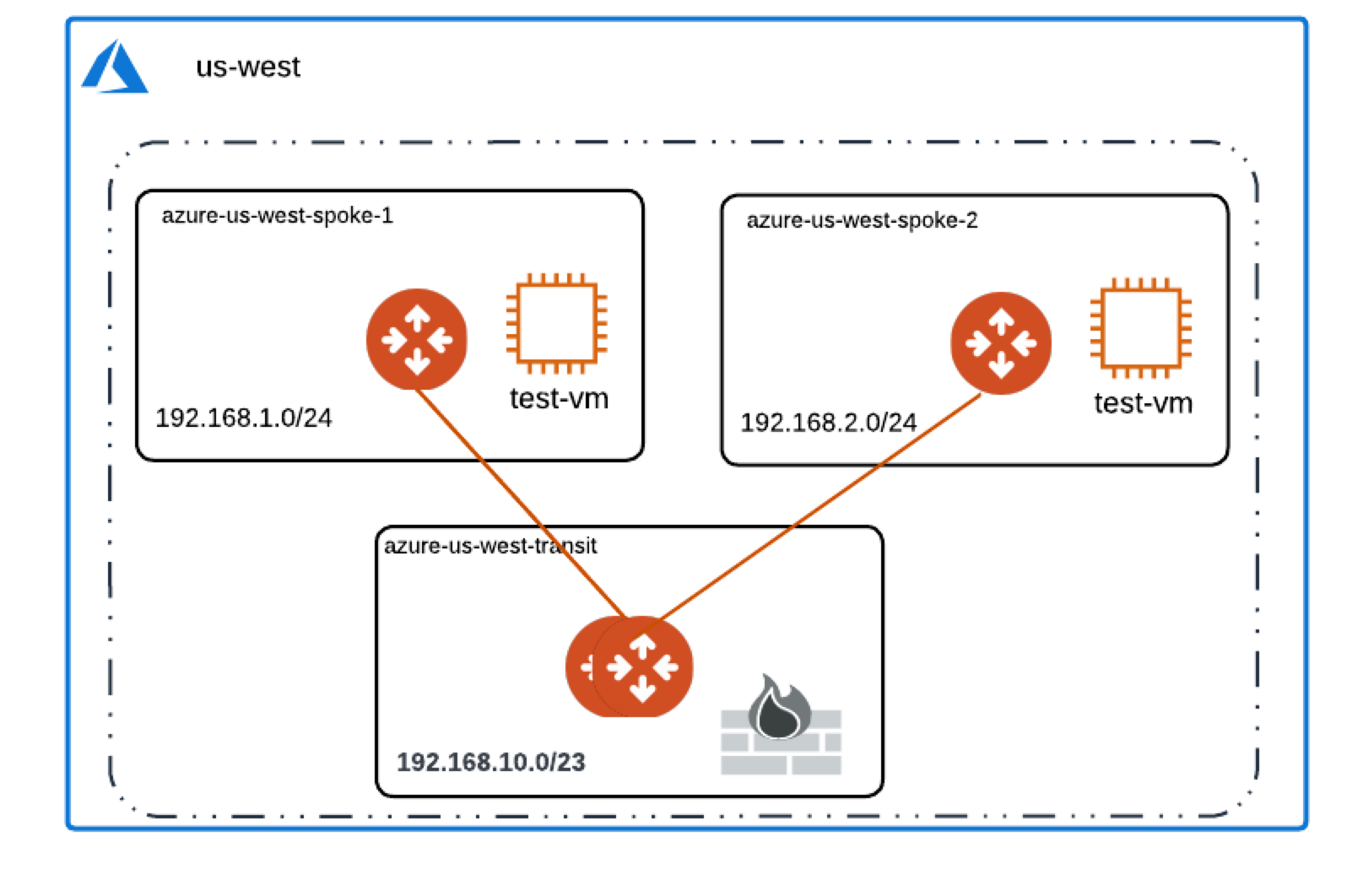
Configuring Palo Alto VM-Series in Azure
After you deploy your Palo Alto VM-Series firewall in the Transit VNet, you can use this example to ensure that traffic is inspected between Spoke VNets using firewall policies.
In Azure, you can scale firewall deployment to multiple Availability Zones and multiple instances/VMs in a maximum throughput Active/Active state without SNAT.
| You must first have launched a firewall instance in the cloud portal. |
For more information on using a bootstrap configuration to set up your Palo Alto firewall in Azure, click here.
For Palo Alto example configurations in other clouds, see:
The three Palo Alto VM-Series interfaces are:
| Palo Alto VM Interfaces | Description | Inbound Security Group Rule |
|---|---|---|
eth0 (on subnet -Public-gateway-and-firewall-mgmt) |
Management interface |
Allow SSH, HTTPS, ICMP, TCP 3978 |
eth1 (on subnet -Public-FW-ingress-egress) |
Egress or Untrusted interface |
Allow ALL |
eth2 (on subnet -dmz-firewall_lan) |
LAN or Trusted interface |
Allow ALL (do not change) |
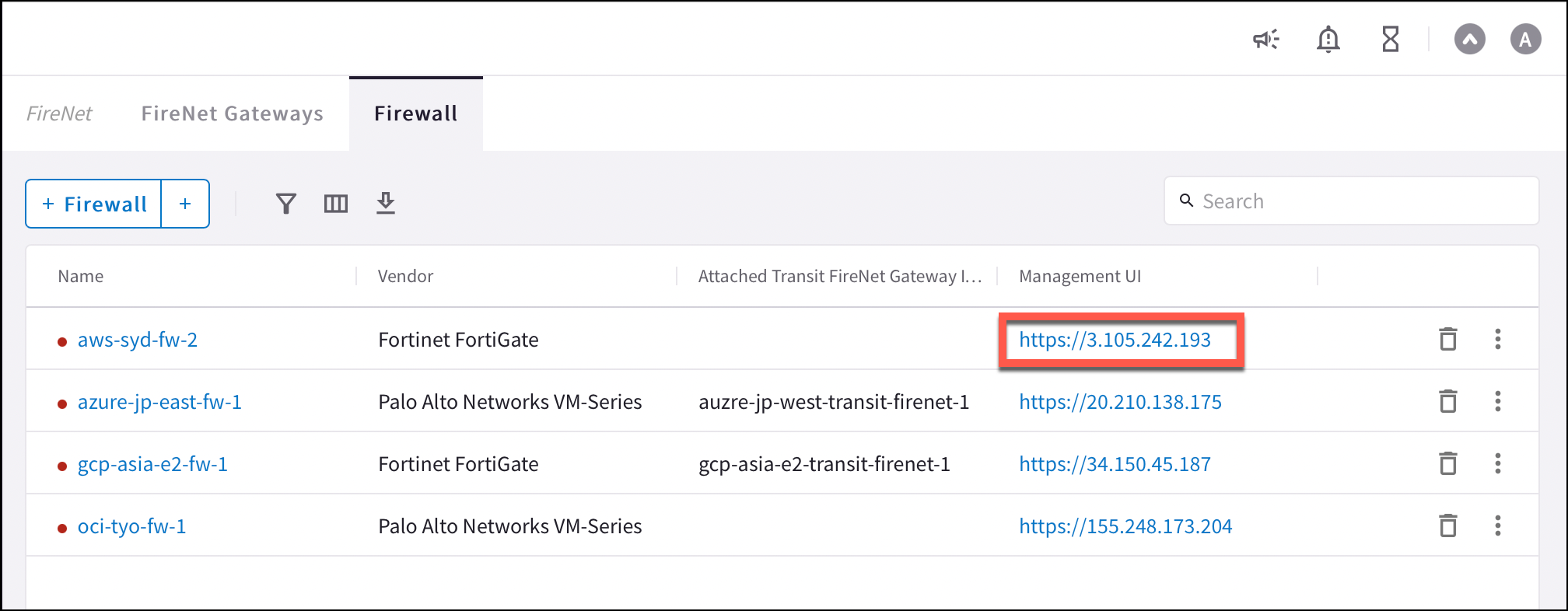
Logging into the VM-Series
Click the Management UI link on the FireNet tab to access the UI of the Palo Alto VM-Series firewall.
Dynamic Updates (all clouds)
To make sure your firewall is up to date, in your firewall UI you can navigate to Device > Dynamic Updates and click Check Now. You can then download and install the latest versions of Applications and Threat Wildfire updates.
Configuring VM-Series Ethernet 1/1 with WAN Zone
WAN is Wide Area Network. Ethernet 1/1 is Management Interface. Provides access to data center applications.
-
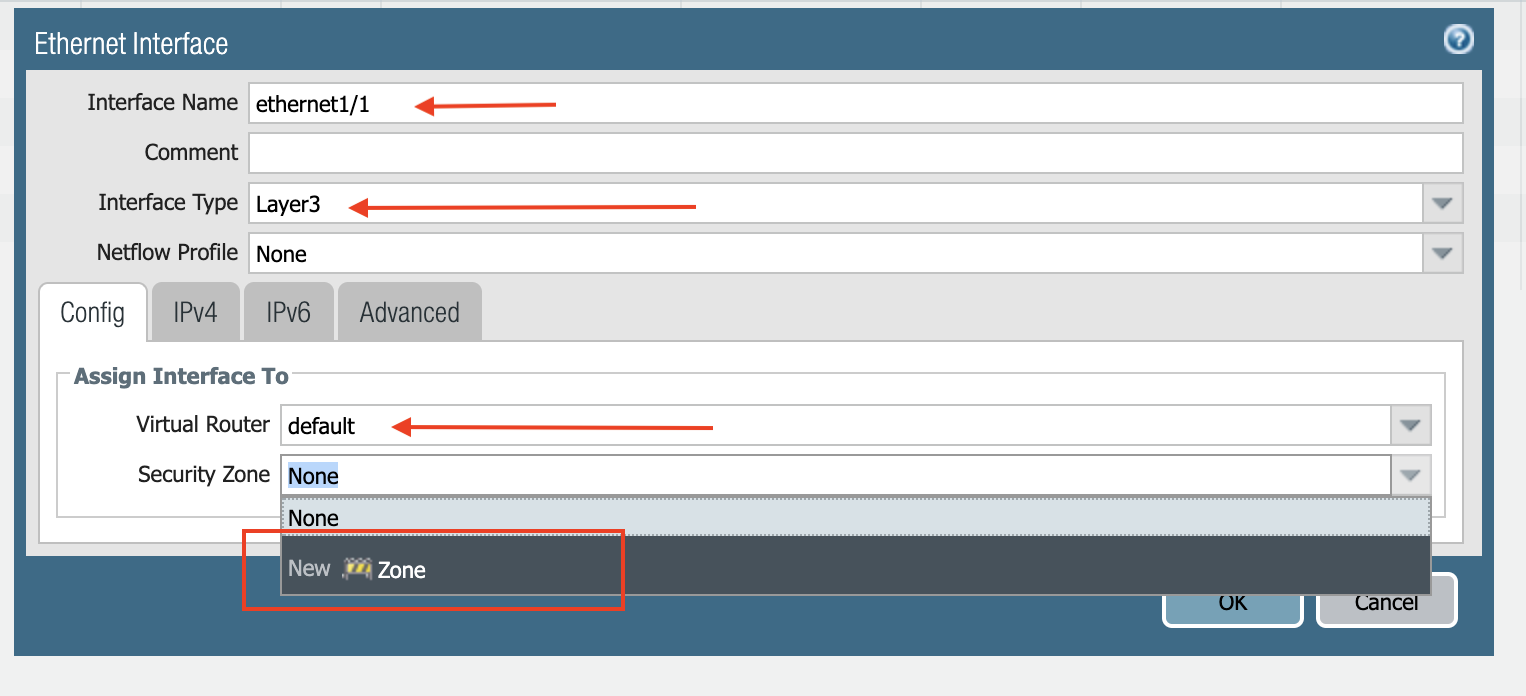
Once logged in, click on the Network tab to see a list of ethernet interfaces. Click ethernet1/1 and configure as per the following screenshot.
-
Select the Network tab.
-
Click ethernet1/1.
-
Select layer3 for Interface Type.
-
Select the Config tab in the popup Ethernet Interface window.
-
Select default for Virtual Router at the Config tab.
-
Click New Zone for Security Zone to create a WAN zone.
-
At the next popup screen, name the new zone WAN and click OK.
-
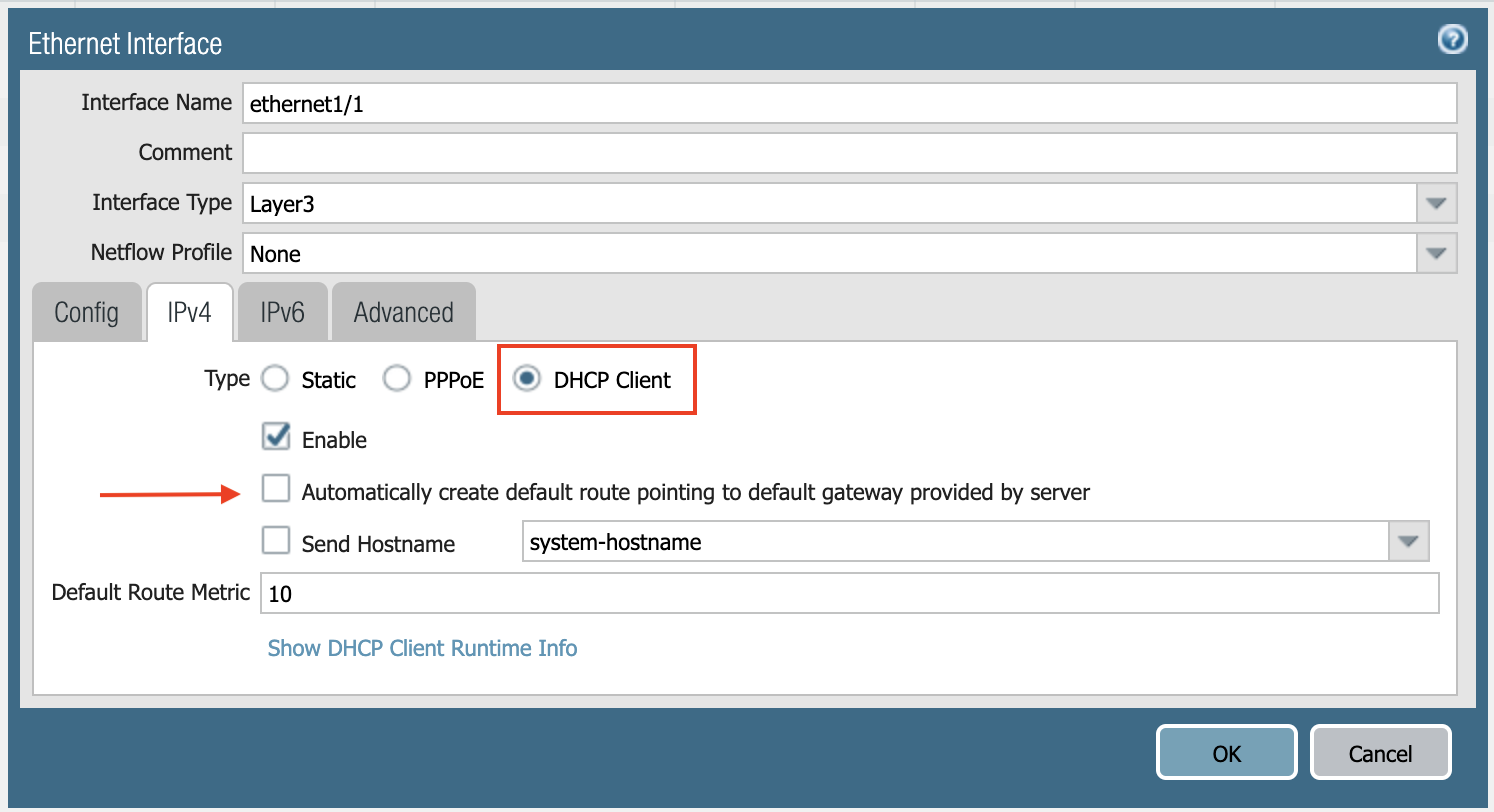
Select the IPV4 tab in the popup Ethernet Interface window.
-
Select DHCP Client.
-
Clear the Automatically create default route pointing to default gateway provided by server checkbox as shown below.
-
Click Commit. Once Commit is complete, you should see the Link State turn green at the Network page for ethernet1/1.
Configuring VM-Series Ethernet 1/2 with LAN Zone
-
Repeat the steps from Configuring VM-Series ethernet1/1 with WAN Zone section above for ethernet1/2. Name the new zone LAN.
-
Click Commit. Once Commit is complete, you should see the Link State turn green at the Network page for ethernet1/2.
Vendor Firewall Integration
Use vendor integration to program RFC 1918 and non-RFC 1918 routes into the firewall.
Enabling VM-Series Health Check
Allowing access to HTTPS or TCP 443 port. not in the AWS procedure for Palo Alto setup.
-
Go to Network > Interface Mgmt under Network Profiles and click Add.
-
Enter a name in the Interface Management Profile, mark the HTTPS checkbox under Administrative Management Service, and click OK.
-
Attach Profile with LAN interface: Network > Interfaces > Select LAN Ethernet Interface > Advanced > Management Profile > Select appropriate profile.
Example for attaching a profile to an interface. Firewall health check probes can be verified in Monitor > Traffic.
Basic Traffic Policy to Allow Traffic VNet to VNet
In this step, we will configure a basic traffic security policy that allows traffic to pass through the VM-Series firewall.
-
Select the Policies tab.
-
Click +Add in the bottom left corner to create a new policy.
-
Select the General tab. Name the policy "Allow-all."
-
Select the Source tab. Select Any for both panels.
-
Select the Destination tab. Select Any for both panels.
-
Select the Application tab. Select Any.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Commit to commit the Allow-all policy.
Configuring Basic Traffic Policy to Allow Traffic VNet to Internet
If you would also like to enable NAT to test egress, follow these steps.
-
Policies > NAT > click Add.
-
Select the General tab, give it a name > click Original Packet.
-
At Source Zone, click Add, and select LAN.
-
At Destination Zone, select WAN. At Destination Interface, select Ethernet1/1, as shown below.
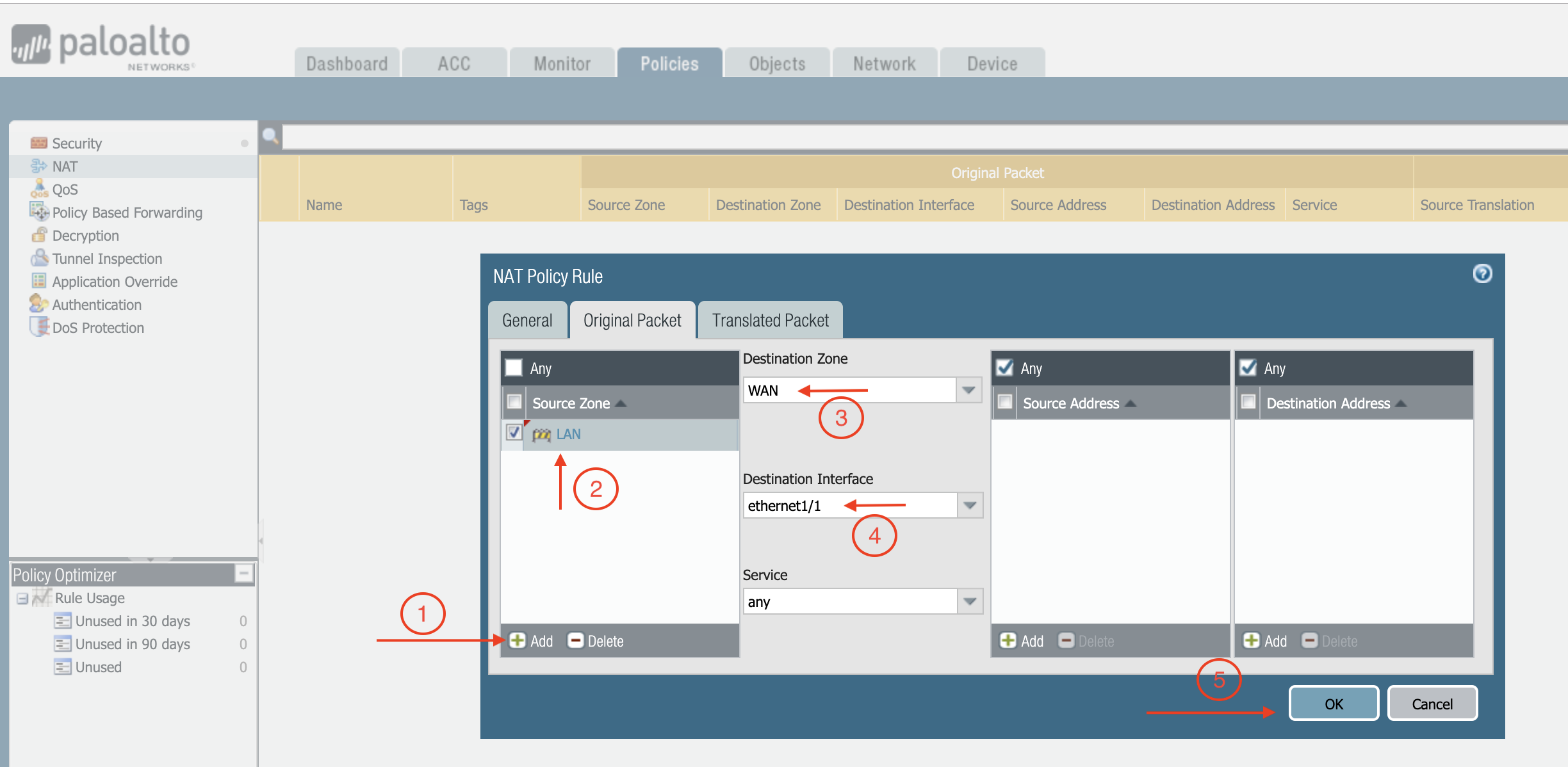
-
Click Translated Packet. At Translation Type, select Dynamic IP And Port.
-
At Address Type, select Interface Address.
-
At Interface, select ethernet1/1, as shown below.
Verifying Traffic Flow
In the VM-Series console, go to Monitor > Traffic. Launch one firewall instance in Spoke VNet-1 and one in Spoke VNet-2.
(Optional) VNet to Internet Traffic
You can inspect VNet to Internet traffic by launching a private instance in the Spoke VNet and pinging packets from the private instance toward the Internet (e.g. 8.8.8.8) to verify the egress function.
| The Egress Inspection is only applicable to VNets that deploy non-public facing applications. If you have any Spoke VNet that has public facing web services, you should not enable Egress Inspection. This is because Egress Inspection inserts a default route (0.0.0.0/0) towards Transit GW to send the Internet traffic toward the firewall to get inspected. Azure’s System Default Route pointing toward the Internet will be overwritten by User-defined default route inserted by the Controller. |